The Precision of Robot Cutting the Small Holes ?
Robot Fiber Laser Cutting Machine.
The precision of robotic systems for cutting small circular holes in metal tubes is generally high,
often achieving tolerances within ±0.1–0.2 mm when using advanced tools like fiber lasers
or high-precision mechanical cutting heads. Robotic systems excel in repeatability
(typically ±0.05–0.1 mm) due to their programmed motion control, making them ideal for complex geometries and consistent batch production.
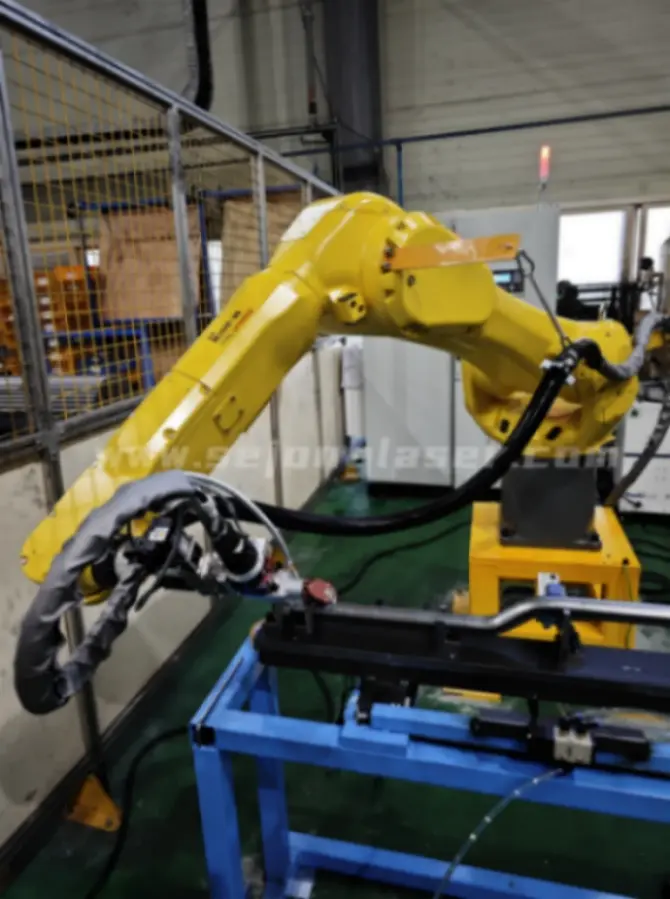

Compared to plasma cutting:
1. Precision:
- Robotic systems (e.g., laser/waterjet): ±0.1–0.2 mm, with minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ).
- Plasma cutting: ±0.5–2.0 mm, depending on torch quality and material thickness. Plasma arcs cause wider kerfs and larger HAZ, reducing edge quality.
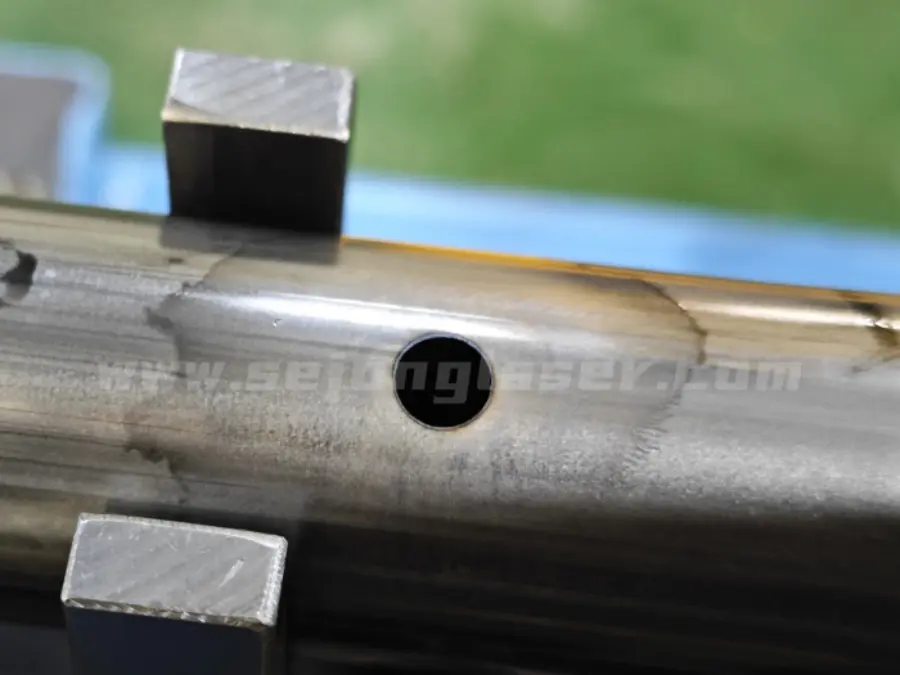

2. Edge quality:
- Robotic laser/waterjet cuts produce smooth, burr-free edges, often eliminating post-processing.
- Plasma cutting leaves dross (slag) and rougher edges, requiring deburring or grinding.
3. Material limitations:
- Plasma works better on thick materials (e.g., >6 mm steel) but struggles with thin-walled tubes.
- Robotic lasers handle thin to medium thicknesses (0.5–20 mm) with superior precision.

4. Speed vs. accuracy trade-off:
- Plasma is faster for thick metals but sacrifices precision.
- Robotic lasers prioritize accuracy, especially for small features like holes.
Summary:
Robotic systems (laser/waterjet) outperform plasma in precision and edge quality for small holes in metal tubes, but plasma remains cost-effective for thicker materials where precision is less critical.